 The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) takes on technological issues associated with microgrid-based energy-efficient buildings in a recently released special edition of Proceedings of the IEEE. The issue’s 11 research papers cover topics ranging from an analysis of geo-referenced building data in evaluating thermal microgrids and automated demand response (DR) systems in smart buildings and microgrids to envisioning changes in behavior as the evolution towards consumer-centric power grids continues.
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) takes on technological issues associated with microgrid-based energy-efficient buildings in a recently released special edition of Proceedings of the IEEE. The issue’s 11 research papers cover topics ranging from an analysis of geo-referenced building data in evaluating thermal microgrids and automated demand response (DR) systems in smart buildings and microgrids to envisioning changes in behavior as the evolution towards consumer-centric power grids continues.
In one research paper, J.Y. Joo and M.D. Ilić present a framework that smart building and microgrid managers can use to build an information exchange supporting their participation in demand-response microgrids. In another, S. Chatzivasileiadis and others present a modular IT platform that enables end-users to better understand the interactions between DR strategies, building comfort levels, communications networks, and power grid operation.
Collectively, ¨the invited papers encompass the latest research on the emerging topic of energy in commercial, residential, and other types of buildings and facilities from respected leaders in the field,¨ explains Boston University’s John Baillieul, an IEEE Life Fellow and one of the special issue’s three editors.
Microgrids and Smart, Energy-efficient Buildings
Integrated smart buildings and microgrids can offer ¨high-bandwidth data exchange between pools of smart, grid-friendly appliances, a smart building operator (SBO) operating within a building automation system (BAS), and an independent system operator (ISO) who communicates requests for demand response as needed to keep the neighboring distribution network operating securely,¨ says Baillieul.
¨By appropriately implementing a Smart Building Operator (SBO) within a building automation system (BAS), recent research has shown that energy distribution through facility microgrids can be simultaneously optimized for efficiency, occupant comfort, and the building’s ability to participate in demand response power markets.¨
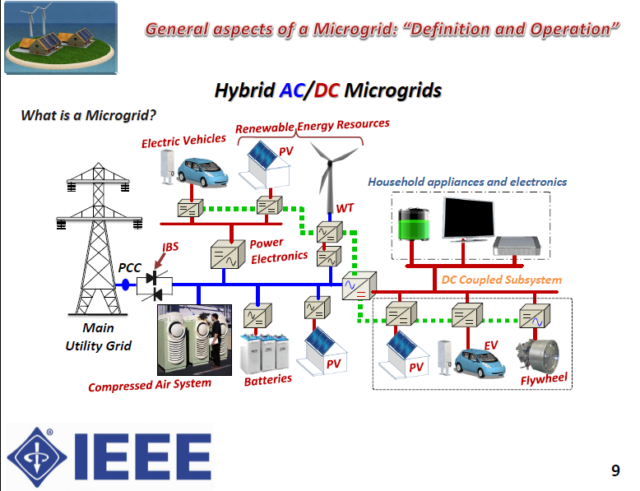
The 11 research authors who contributed to the Proceedings of the IEEE special issue were chosen specifically for their experience and knowledge in the diverse aspects of designing, building, and operating smart building energy management and microgrid systems. The overarching goal was ¨to bring this diverse but interrelated expertise into focus in a single volume,¨ says Bailleul.
Baillieul notes that power and energy have been a primary focus of the IEEE since its inception in 1884, when Thomas Edison and partners created the American Institute of Electrical Engineers. Today, the field is in a state of high flux given rapidly falling costs and growth of distributed power generation, including residential and commercial solar PV systems, electric vehicles (EVs), battery-based energy storage, and bi-directional smart grid energy management systems.
These factors have led to the emergence of a growing class of local renewable energy ¨prosumers¨ and poses fundamental challenges to grid operators given the intermittent nature of solar and wind energy resources, according to Baillieul.
¨Because the Proceedings of the IEEE reaches a broad audience of technically literate readers,” explains Baillieul, “it was deemed to be an ideal medium through which to communicate important new research on the operation of next-generation microgrids — especially those found in new residential and commercial buildings.”

Microgrid Integration in Smart Buildings is the Best Strategy.