Microgrids
» North America
– US Marine Corps, Sandia National Labs Team Up on Microgrids, Renewable Energy
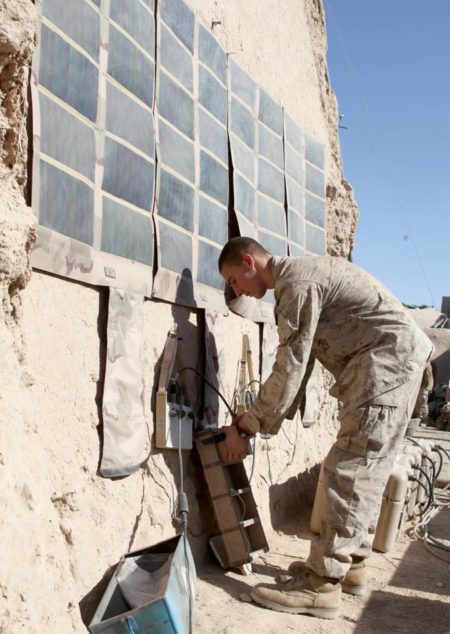

*US Marine Corps
Researchers from the US Department of Energy’s Sandia National Laboratories are working with the US Marine Corps to develop highly reliable, readily accessible and cost-effective alternative energy systems, including microgrids and renewable energy systems, according to a May 5 press release.
¨An army marches on its stomach,¨ states an oft-cited Napoleon Bonaparte quote. About a century and a half later, events in the Black Sea region during World War II demonstrated just how critical petroleum had become in military operations.
Today, the federal government and US military are at the forefront of the transition to emissions-free energy alternatives as they strive to reduce fossil fuel dependence and enhance energy security and its overall effectiveness. These goals guide and inform the new Marine Corps-Sandia partnership. The two organizations aim to develop new analytic software tools that will enable decision-makers in the Marine Corps to achieve their long-term renewable energy goals.
“We are honored to partner with the United States Marine Corps,” Sandia project lead Nadine Miner says. “The modeling and optimization suite of tools that Sandia has developed will provide the Marine Corps with the information they need to help make decisions about which renewable energy technologies to invest in. The tools will also help them understand the impacts of their decisions. This project will help the Marine Corps invest taxpayers’ money wisely.”
– US Navy Deploys Microgrid at Maine Shipyard
Ameresco’s Federal Solutions Group successfully demonstrated GE’s Microgrid Control System (MCS) at the Portsmouth Naval Shipyard in Kittery, Maine, according to a May 3 press release. GE Grid Solutions’ MCS and a 500-kW/580-kWh battery energy storage system (BESS) tapped into on-site generation, including a 10-MW Combined Heat & Power (CHP) plant and a 4-MW emergency back-up generator.
The project team conducted two live tests that simulated a base-wide grid outage. The microgrid successfully shed nonessential loads and powered essential systems during the outage.
“Ameresco is excited the microgrid functioned as designed and the tests at PSNY were highly successful,” Ameresco Federal Solutions’ SVP Nicole Bulgarino says. “Given the success of this initiative, the potential for broad application of this system across US government installations and other organizations is very promising, particularly at a time when resiliency has become a key concern.”
– MIT Team Wins University’s Clean Energy Prize for Microgrid ¨Brain¨
Fielding a team comprised of MIT students and alumni, Heila Technologies outdid five other finalists to win and take home $100,000 during the Cambridge, MA-based university’s ninth annual Clean Energy Prize Competition, MIT News reported May 2.
Heila’s team won the Grand Prize, which was presented by National Grid, for developing a universal control hub that automatically monitors and manages disparate microgrids – such as those connected to solar PV systems, wind power installations and gas-fired generators that power campuses, military bases, and off-grid communities.
“A big problem we’ve seen in microgrids is, when you buy them, you can’t get them to work together,” John Donnal, a Ph.D. student in electrical engineering and computer science, explains. “Now you, as a customer, can go out and find the best industry player to get the [microgrid] equipment, and you get Heila to get them to all talk to each other. And when you can make microgrids that easy, you can then integrate renewables at a much higher rate.”
» International
– University of Washington Student-Led Company Bringing Solar Microgrids to the Congo
Rich in mineral and energy resources, reliable, affordable access is sadly lacking in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) and other sub-Saharan African countries. That’s changing as entrepreneurial startups are integrating solar PV, lithium-in battery storage, and mobile payments technology in Cloud-based distributed energy management platforms.
NovoMoto, an award-winning startup that’s led by University of Washington students, is readying a roll-out of its remotely controlled solar energy kiosks and microgrids in the DRC, according to a May 6 news report.
“Depending on the area of the country, people now pay $15 to $22 a month for kerosene and mobile phone charging,” NovoMoto co-founder Aaron Olson says. “We beat it by providing electricity for $9 a month; that’s a savings of 40 to 60 percent.”
An estimated 59 million Congolese lack access to reliable grid electricity. They rely primarily on kerosene to meet their lighting needs. Kerosene typically costs 25-30% of residents’ monthly income and poses human and environmental health and safety risks. Moreover, the quality of lighting provided is often poor.
NovoMoto believes its solar-storage kiosks and community microgrids offer a safer, environmentally friendly and cheaper alternative. Plans are to start rolling out solar energy storage kiosks and then move on to MicroPlant microgrid systems in off-grid communities.
– UNDP, Bank of Industry Commission Nigerian Solar Microgrid Project
The United Nations Development Program (UNDP) and Nigeria’s Bank of Industry (BoI) commissioned a 24-kW solar microgrid for the Obayantor 1 community in the state of Edo, according to a May 3 news report.
The ¨pay as you go¨ solar microgrid brings affordable, reliable access to electricity to communities that haven’t enjoyed the benefits electrical power brings before, and it does so in an environmentally friendly way, BoI managing director Waheed Olagunju says.
“We are all aware that power remains a major obstacle to growth in Nigeria, as inadequate and unreliable electricity undermines investment opportunity, economic growth, social and infrastructure developments,” Olagunju explained.
BoI plans to roll out similar emissions-free microgrids in Edo State in collaboration with the state government.
Policy, Markets, and Investments
– Oracle Buys Opower
*Opower
IT giant Oracle announced it’s acquiring smart grid data analytics specialist Opower for $532 million, according to a May 2 news report.
The acquisition highlights the potential symbiosis that exists between distributed energy, smart grid and ICT industry companies. Expected to be finalized later this year, Oracle’s purchase price came in at a 30% premium to Opower’s share price as of stock market close on Friday, April 29.
Arlington, Virginia-based Opower monitors, tracks, and analyzes energy usage in tens of millions of homes across the US. More than 100 utilities, including PG&E and Exelon, make use of its platform and services, according to the news report.
“While energy efficiency has historically been the primary driver of new client acquisition, this year was the first time we saw customer care fuel a significant number of deals,” said Opower CEO David Yates.
“The move to the cloud is a generational shift in technology that is the biggest and most important opportunity in our company’s history,” Oracle CEO Safra A. Catz explained.
– ¨Charge¨ Campaign Aims to Boost Renewable Energy in Montana
The global drive to reduce greenhouse gas emissions is taking its toll in states and communities where coal mining companies have traditionally been the biggest employers and sources of local government revenue. Renewable energy advocates and businesses in Montana are responding with a public campaign, dubbed “Charge,” to foster development of renewable energy resources, according to an April 30 news report.
Organizers have launched a website, produced bumper stickers, and plan to paper billboards with photos of a wind farm and the slogan: ¨A Boom That Won’t Bust.¨
“Montana’s energy economy is in crisis,” says Jeff Fox, Montana policy manager for Renewable Northwest. “West coast states have made the decision to reduce or eliminate coal-produced energy, and that means eventually Montana will either need to decide what to do without coal jobs and revenue or find a sustainable replacement.”
» International
– Prospective Buyers Rush into Spain’s Renewable Energy Sector
Investment funds and renewable energy companies from around the world are scouting Spain’s renewable energy sector for acquisitions, according to a May 1 AFP news report.
Spanish renewable energy companies continue to struggle amid sharp cutbacks Spain’s feed-in tariff (FiT) and government efforts to recapture some of the payments made. The national government’s FiT program proved unsustainable amidst the global financial crisis and recession that originated in the US in 2008-2009. That said, Spanish renewable energy companies number among the largest and most experienced in the world.
This confluence of factors has attracted renewable energy companies and investment funds looking to make acquisitions. They ¨have been on a buying spree, taking advantage of the know-how and growth prospects of a sector still limping out of a crisis,¨ states Phys.org’s news report.
The biggest acquisition in 2015 by far was US private equity firm Cerberus’s purchase of Renovalia for about 1 billion euros. The value of all transactions in 2015 reached 5 billion euros ($5.7 billion), according to an energy analyst at Roland Berger in Madrid.
Climate Change
– Florida’s Coral Reef Disappearing Faster than Thought

* University of Miami
A new study published in the May 2 edition of Global Biogeochemical Cycles reveals that Florida’s coral reef – the only living one in the continental US – is starting to dissolve due to ocean acidification.
Conducted by a team of researchers from the University of Miami’s Rosenstiel School of Marine & Atmospheric Science, the study is the first to document the effects of increasing ocean temperatures and seawater acidity along Florida’s coral reef.
“We don’t have as much time as we previously thought,” says senior author Chris Langdon, a University of Miami Rosenstiel School professor of marine biology and ecology. “The reefs are beginning to dissolve away. This is one more reason why we need to get serious about reducing carbon dioxide emission sooner rather than later. The worst bleaching years on record in the Florida Keys were 2014-2015, so there’s a chance the reefs could be worse now.”
– Scientists Warn of Effects of Lower Ocean Oxygen Levels
New research from a team at the US National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) warns that lower levels of oxygen in ocean waters could pose a greater problem than previously believed in little more than a decade, according to a May 4 news report.
“Loss of oxygen in the oceans is one of the serious side effects of a warming atmosphere and a major threat to marine life,” says study lead author Matthew Long. “Since oxygen concentrations in the ocean naturally vary depending on variations in winds and temperature at the surface, it’s been challenging to attribute any deoxygenation to climate change. This new study tells us when we can expect the effect from climate change to overwhelm the natural variability.”
The research results are another indication of the threats and costs rapid climate warming pose to societies and all life on the planet. That said, the prospective effects are so numerous, varied, and widespread that climatologists and other scientists involved in climate research emphasize the need for governments and societies to do more to support research efforts.
“We need comprehensive and sustained observations of what’s going on in the oceans to compare with what we’re learning from our models, and to understand the full effect of a changing climate,” Long explained.
