Microgrid News
» North America
– ARPA-E Funds Texas ¨Internet of Energy¨ Microgrid Project
Microgrids and the power industry are at the center of the boom in Internet of Things (IoT) technology and investment. ARPA-E in December announced $33 million in NODES (Network Optimized Distributed Energy Systems) funding for 12 projects that aim to develop innovative hardware and software that integrate and coordinate grid generation, transmission and end-use energy systems.
One of the 12 is taking place in Lubbock, Texas, where DNV GL, Group NIRE and Geli (Growing Energy Labs, Inc.) will develop and operate an ¨Internet of Energy¨ (IoEn) platform that integrates management of as many as 100 distributed energy resources (DER) with an eye towards enabling utilities to rapidly integrate large-scale renewable power generation capacity.
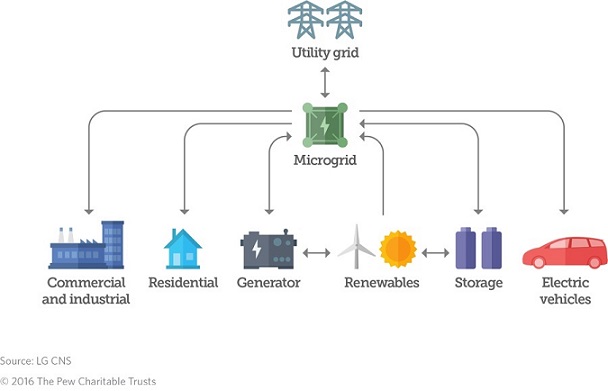
– Connecticut Neighborhood Microgrid Project Breaks Ground
Exelon Corp. subsidiary Constellation and Bloom Energy broke ground on a neighborhood fuel cell-based microgrid in Hartford, Connecticut, the companies announced April 13.
The 800-kilowatt (kW) microgrid is designed to meet all the electricity needed by Parkville Elementary School, Dwight Branch Library, Parkville Senior Center and Charter Oak Health Center. It also will serve as an emergency source of electrical power for these facilities, as well as a local fuel station and grocery store. Any surplus electricity produced will reduce costs at four local schools: Bulkeley High School, Hartford High School, Weaver High School and the Sport and Medical Sciences Academy, the project partners highlight.
– Multi-source AC/DC Microgrid Project Launches in Ontario
Canada’s ARDA Power and Austria’s Gildemeister GmbH have joined in a DC-linked microgrid project in Burlington, Ontario that is to incorporate multiple energy sources – solar and gas-fired generation among them – energy storage, and both AC and DC current and loads.
All of these are to feed into a single DC bus via the ARDA DC Microgrid Platform. Gildemeister is providing energy storage capacity with its 20kW/100kWh CellCube flow battery system, to which an ARDA Battery DC-DC converter will be added.
» International
– Solar Proving Popular among Rural Sub-Saharan Africans
A growing set of innovative solar energy startups have been bringing electricity where it’s never been before – rural communities in sub-Saharan Africa. Not only is it affordable, it’s cheaper than the kerosene or charcoal typically used in homes and villages for lighting – not to mention a helluva lot safer and environmentally friendly.
Okay, rural sub-Saharan Africans’ daily electricity use is only a small fraction of what the average American consumes, but these are people who haven’t enjoyed all the benefits readily available electricity can provide. Reports have noted that children’s school grades are on the rise, and residents – women in particular – are starting small sideline businesses by offering to charge people’s cell phones – a task that for many involves walking many miles and then waiting in line.
In an April 12 Treehugger post Derek Markham provides a brief profile of Powerhive, a young socioeconomic development-minded company that’s building on its initial success in Kenya. Powerhive is one of several home solar PV vendors that has combined PV, battery-based energy storage and mobile payments and networking to build a business that’s making a powerful, positive impact on the lives of rural Kenyans.
Makes you wonder why the same thing isn’t happening outside of sub-Saharan Africa, across Central and South America and the Caribbean, for instance.
– Indian and Canadian Organizations Sign Microgrid MoUs
A Canadian international trade mission to India resulted in the signing of two microgrid Memorandums of Understanding (MoU), The Economic Times of India reported April 13.
IT services specialist Tech Mahindra’s new microgrid-as-a-service unit and Ontario’s Advanced Energy Center signed an MoU with the Himachal State Electricity Board to help improve grid reliability in the state’s remote areas. Tech Mahindra also signed an MoU with Ryerson University’s Center for Urban Energy. The two will carry out advanced microgrid research.
Policy & Markets
– The Cost, and Returns, of ComEd’s Illinois Smart Grid System
ComEd on April 13 filed a service rate hike request with the Illinois Commerce Commission that would add an average of about $2 to customers’ monthly utility bills, the Chicago Sun Times reported. Totaling some $138 million, the proposed rate hike would cover the costs of ComEd’s smart grid investments.
In addition, ComEd filed a proposal with the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) requesting an increase in transmission rates that would add around another $1 to residential customers’ bills beginning this June.
ComEd pointed out that some of the costs – some $3 a month – will be offset by lower electricity costs resulting from deploying smart meters and automated metering infrastructure (AMI), as well as building out neighborhood/community microgrids.
ComEd’s Smart Grid system is providing record power reliability even as the roll-out continues, avoiding millions of outages and shortening grid restoration times when outages do occur, the utility highlighted. ComEd has installed more than 2 million smart meters at customer sites thus far.
– First Paid P2P Microgrid Energy Transaction Moves Utilities Out of the Frame
TransActive Grid on April 11 announced the first paid P2P energy transaction crossed its microgrid energy trading platform. One member of the Brooklyn Microgrid – former DOE Energy Star national director Bob Sauchelli bought surplus electricity generated from another – social justice activist Eric Frummin. The precedent-setting P2P energy transaction is ¨a giant step towards a consumer-run future,¨ Transactive Grid stated in a news release.
The precedent-setting P2P local energy transaction bypasses utilities, enabling local consumers and ¨prosumers¨ to connect with one another and participate directly in the process of producing, distributing and consuming emissions-free electrical power.
– Residential Time of Use Pricing: Getting it Right
In an April 14 EDF Voices blog post energy economist Jamie Fine reviews and expands on a Vox article by David Roberts that advocates making new grid interconnections as a means of getting the most out of ongoing growth in California’s solar energy production.
Occasionally, solar energy installations in California produce so much electricity the the state’s grid has reached, even exceeded, full capacity. (Who would have thunk that 10, or even 5, years ago?) Grid managers ¨curtail¨ solar energy production when this happens, which means all that emissions-free electricity goes to waste, Roberts explains.
Roberts focuses on making regional grid interconnections as a means of resolving the issue, which is expected to intensify as more solar energy comes online and California’s utilities to meet a recently revised state mandate of renewables accounting for 50% the electricity they purchase by 2030.
While Fine agrees that making new interconnections with grids in neighboring states makes good sense, he doesn’t see it a long-term solution. He highlights another means by which California can make better use of all that solar power: time-of-use pricing (ToU).
Community Solar
– Washington Community Solar Incentives Overgenerous?
Washington may have been a bit too generous when it enacted share, community incentives, Know.org’s Tom Banse reported April 13. Thousands of state residents have bought shares in local community solar projects developed by their utility or a local non-profit since the incentives were introduced.
Indicative of residents’ strong interest in participating in shared solar power generation, twice as many people filed applications to buy shares in a community solar rooftop array developed by Mason County PUD (Public Utility District) #3 than were available.
The local utility estimates that thanks to the state incentives, the community solar project’s payback period will be just 3-4 years as opposed to anywhere from 10-15 years for a residential solar installation. More than 50 other shared, community solar projects have been registered in Washington to date. The surge has led more than 12 state utilities to cap incentive payments.
A proposed bill to lower subsidies for new projects in return for raising the cap didn’t pass a vote in the state legislature. Utilities, meanwhile, are notifying community solar project owners their annual incentive checks could be reduced because their programs are oversubscribed.
Energy Storage
– Lithium-Ion Battery Storage Market Revenues Forecast to Exceed $28 Billion
The global market for lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery technology will increase at a 10.8% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) from 2016-2022, according to Allied Market Research (AMR). Total market revenue will reach $46.21 billion.
Growing use of Li-ion batteries in the automotive sector will fuel market growth, according to AMR. Other contributing factors are: increased demand from smartphone, tablet and other CE product manufacturers, new regulations aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions, pollution levels and increasing energy efficiency.
