>> Microgrids
*Philadelphia Navy Yard, Credit: Microgridprojects.com
– Portsmouth Naval Shipyard Likes Results of Two Microgrid Tests
Two live microgrids have been undergoing testing at the naval shipyard in Maine, a project through which the US Navy plans to avoid losing electrical power during local grid outages. The broad goals of the program are to identify cost-effective technology that enhances energy security, reliability, resiliency of electricity services on military bases, as well as provide ancillary services to the grid Independent Systems Operator (ISO). Ameresco and GE joined to design, install, and demonstrate the two microgrids with funding from a Department of Defense (DOD) Environmental Security Technology Certification Program (ESTCP) grant.
“Given the success of this initiative,” explains an Ameresco spokesperson, “the potential for broad application of this system across U.S. Government installations and other organizations is very promising particularly at a time when resiliency has become a key concern.”
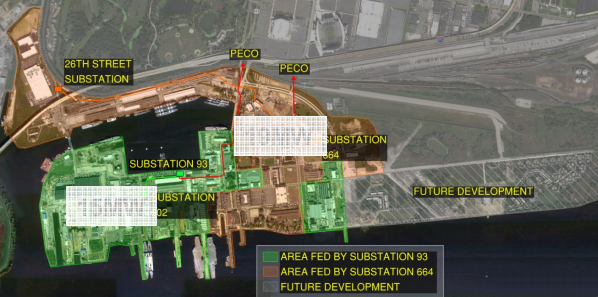
– PECO Pitches Grid-Connected Community Microgrid Projects
The Exelon-owned regulated electric utility submitted its connected microgrid project plans to Pennsylvania regulators May 18. The two integrated community microgrids are intended to enhance power supply resiliency in densely populated neighborhood with loads averaging around 8.6 MW, a news report explains.
Dubbed the PECO Microgrid Integrated Technology Pilot Project, the integrated community microgrids will supply electricity across a 388-acre area of Concord Township. The area is home to public and emergency/disaster recovery facilities including healthcare clinics, emergency services, a retirement community, hotels and fuel stations.
“Severe weather is a leading cause of power outages in PECO’s service territory. For example, as a consequence of Hurricane Sandy in 2012, approximately 850,000 PECO customers experienced interruptions of service, some for as many as eight days,” PECO elaborated in its Pennsylvania Public Utility Commission regulatory filing.
– Partners Raise Equity Capital for 50 MW of Texas Microgrids
Balfour Beatty Infrastructure Partners LP (BBIP) and Enchanted Rock (Erock) on May 26 announced they had raised enough equity capital to complete a fund that will finance construction of microgrids in Texas. The partners has signed 50 MW of microgrid customer contracts that will be used to finance microgrid installations for commercial and industrial (C&I) facilities.
The C&I microgrids will be built, owned and operated by newly formed limited liability company (LLC) Texas Microgrid. Making use of high-efficiency, low-emissions natural gas generators, the C&I microgrids will serve as emergency back-up power sources, according to the press release.
Texas Microgrid and its C&I microgrid customers will also be able to earn revenues by selling electricity and providing ancillary grid services to ERCOT, the state’s largest grid operator.
– Renewable Microgrid to Power Hawaii Clean Energy Conference
An all-renewable-energy microgrid will be used to power the Asia Pacific Clean Energy Summit in Honolulu June 21-23, according to a news report.
OpTerra Energy Services is responsible for overall microgrid project management. It will also deliver and install an EV charging station. All Power Labs will deliver and install a biomass gasifier, Blue Planet Energy a lithium-ion battery energy storage system, SunPower and Solexel a solar PV array and Spirae its Wave Microgrid controller.
Data from the emissions-free microgrid platform will be used to model resilience, interoperability, efficiency, and other key attributes that illustrate conference themes. The demonstration, data, and analysis should also prove useful for Hawaii as the state works to achieve its goal of 100% renewable energy by 2045.
>> International

*PowerGen Kenya
– Kenyan Solar Microgrid Startup Looks to Break State Utility Monopoly
Nairobi-based PowerGen is seeking approval from Kenya’s Energy Regulatory Commission (ERC) to generate, supply, and sell power to homes using its solar-energy microgrids, according to a news report.
If approved, PowerGen would become just the second private company with permission to generate and sell electricity to residential customers in Kenya. Another solar energy-based community microgrid provider, Powerhive, was the first. US-based Powerhive’s microgrids are supplying affordable emissions-free electricity to more than 1,500 rural households in Kisii, and the company plans to expand to 100,000 more in western Kenya this year.
PowerGen intends to invest up to $10 million in the construction of microgrids to supply off-grid power for rural communities. Solar microgrids are the fastest route for Kenya is to achieve its goals of all homes having access to affordable electricity supply by 2020.
>> Solar PV, Energy Storage
– Adding Storage to Multi-Family Housing Could Double Solar PV Savings
A research report produced by the Center for Sustainable Energy, the California Housing Partnership Corp., and Clean Energy Group concludes that adding battery energy storage to multi-family housing solar PV systems would far outweigh the costs and as much as double energy bill savings.
The combination of solar PV and battery energy storage could nearly wipe out utility electricity use and bills for some residents in two utility studies, according to the ¨Closing the California Clean Energy Divide¨ report. More broadly, adding battery energy storage at affordable multi-family housing sites would give renters some influence and a sense of participation in determining how the electricity they use is produced, as well as gaining some degree of control over how much they spend on electricity.
According to an analysis of actual data from existing buildings: “…adding battery storage to a solar PV system installed on an affordable housing property in Southern California could increase the annual savings on a property owner’s electricity bill to 99%, which is nearly double the savings of what a solar-alone system can provide.”
> International

*Credit: Telesur, EFE
– Some 2 Million Rural Mexicans Could Benefit from New Solar Installations
Residential solar installation companies are installing solar PV systems in rural areas of southern Chiapas and Oaxaca states, home to the largest population of indigenous peoples in Mexico. As many as 2 million rural residents are poised to benefit, according to a news report.
Solar PV systems provider Enlight has launched a program in partnership with social enterprise Ilumexico promoting solar energy development in both rural and urban areas. Under the program, the more systems the partners install in major cities such as Mexico City and Guadalajara, the more funding goes towards installing single-family PV systems in rural communities.
In addition to installing the rural home solar PV systems, the program partners are providing training for local residents that will help stimulate sustainable social and economic development and help Mexico reach its national climate change and renewable energy goals.
>> Policy, Markets, and Investment
The California Energy Commission (CEC) hosted a microgrid development roadmap workshop May 24. The workshop is part and parcel of CEC’s aim of fostering growth in commercial microgrid installations, according to a news report.
The commission has identified the interconnection, communication, and control technologies to be incorporated in its state-wide microgrid commercialization roadmap as well as regulatory barriers that constrain project investment and development.
Representatives from CEC, the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC), and the California Independent Systems Operator (CAISO) are discussing how stakeholders – project developers, utilities, community groups, and manufacturers – can help remove barriers to commercial microgrid deployments.
>> Water, Energy, and Natural Resources
– Lake Mead Water Level Hits Lowest Ever
Lake Mead, the U.S.’ largest reservoir located in Nevada and Arizona, has hit its lowest water level to date. The new low (1,074.6 feet) is a level not seen since the original filling of the reservoir in the 1930s. Lake Mead’s low is the latest dramatic illustration of an ongoing rapid decline set against a backdrop of regional population growth, urbanization, and climate change.
The new low raises the likelihood the federal Interior Department will institute emergency rationing restrictions on draw-downs in Arizona, Nevada, and California, according to a news report. A water shortage will be declared should Lake Mead’s water level register below 1,075 feet in 2017.
“This problem is not going away and it is likely to get worse, perhaps far worse, as climate change unfolds,” says Brad Udall, a senior water and climate research scientist at Colorado State University. “Unprecedented high temperatures in the basin are causing the flow of the river to decline. The good news is that we have time and the smarts to manage this, if all the states work together.”
